정렬되어 있는 배열에서 중복된 값 제거하기
첫번째 풀이
소스 코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
public class RemoveDuplicatesFromSortedArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {1, 1, 2};
// int[] nums = {0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4};
System.out.println("result: " + removeDuplicates(nums));
}
public static int removeDuplicates(int[] nums) {
Set<Integer> items = IntStream.of(nums).boxed().collect(Collectors.toSet());
return items.size();
}
}
풀이
자료구조 Set 을 이용하여 중복되지 않은 값을 넣고 size 만큼 반환하도록 작업
결과
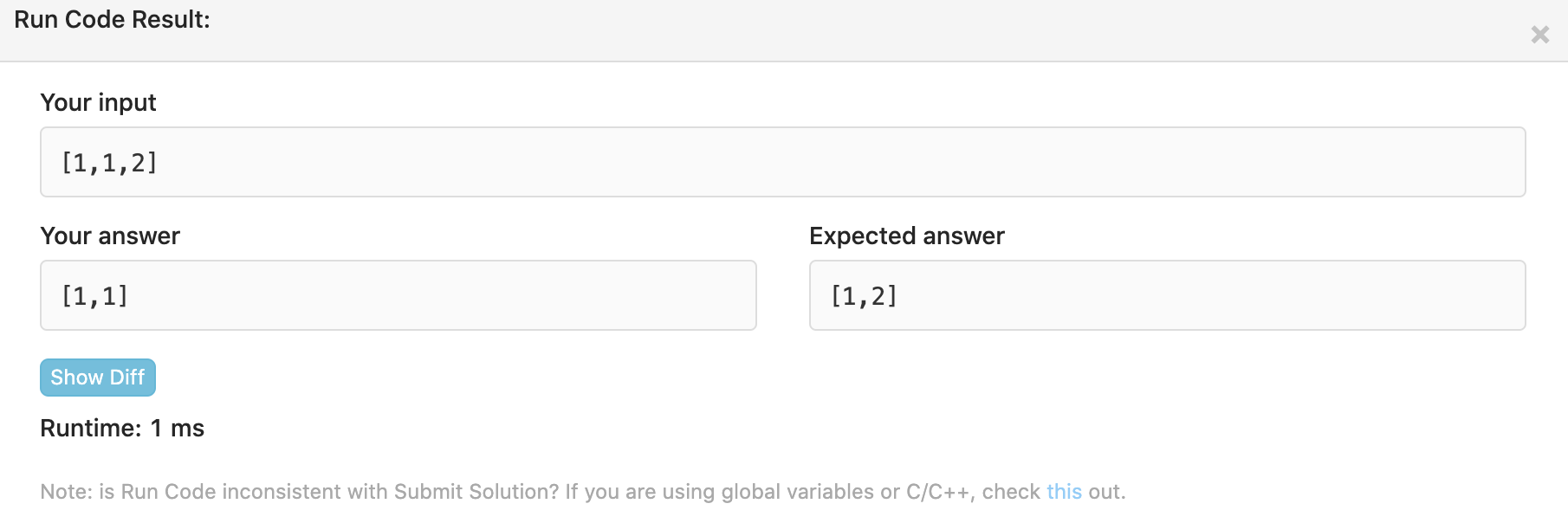
이유 ?
반성 1. 문제를 잘 봐야 한다 ..!
문제의 첫 문장에서 공간복잡도는 O(1) 을 유지해야 한다고 했다.
즉, Set 을 사용하는 순간 공간복잡도가 올라가기 때문에 틀린답일 수 밖에 없다.
반성 2. 이번엔 문제의 설명을 잘 봐야 한다 ..!
// nums is passed in by reference. (i.e., without making a copy)
int len = removeDuplicates(nums);// any modification to nums in your function would be known by the caller.
// using the length returned by your function, it prints the first len elements.
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
print(nums[i]);
}
문제 설명의 이부분이 핵심이다.
함수의 return 값을 통해 nums 배열의 0 ~ return value 까지 for 문을 돌면서 출력하고 그 출력한 값을 비교하도록 되어있다.
즉, 중복되지 않은 값들을 앞으로 빼내줘야 하고 그 위치(index)를 반환해야 한다.
최종 풀이
소스 코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
public class RemoveDuplicatesFromSortedArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {1, 1, 2};
int len = removeDuplicates(nums);
System.out.println("len: " + len);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
System.out.print(nums[i] + ",");
}
}
public static int removeDuplicates(int[] nums) {
int index = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length - 1; i++) {
if (nums[i] != nums[i + 1]) {
nums[index] = nums[i + 1];
index++;
}
System.out.print("cur nums: ");
for (int j = 0; j < nums.length; j++) {
System.out.print(nums[j] + ",");
}
System.out.println();
}
return index;
}
}
풀이
새로운 값이 들어가야 할 위치(index) 를 지정해두고 for 문을 돌면서 같은 값이 아닌 값을 만나면 index 위치에 그 값을 저장하고 index를 증가시켜 위치를 보정
회고
내가 문제를 정확하게 읽지 않은 것도 맞지만 이러한 정답을 제출하도록 하는 문제는 처음인 것 같다.. 알고리즘을 풀 때 첫번째는 문제의 의도 를 파악하는 것이긴 하지만.. 조금 난해한 문제였던 것 같다.