너무 복잡하게 생각하지말고 하나하나 차근차근 풀어야 된다!!
문제 설명
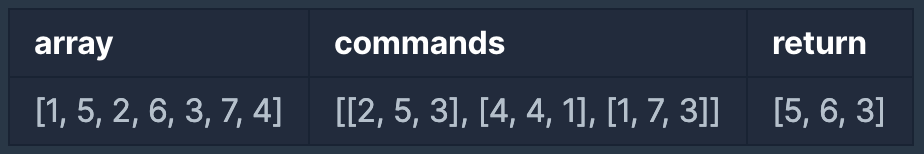
배열 array의 i번째 숫자부터 j번째 숫자까지 자르고 정렬했을 때, k번째에 있는 수를 구하려 합니다.
- 예를 들어 array가 [1, 5, 2, 6, 3, 7, 4], i = 2, j = 5, k = 3이라면
- array의 2번째부터 5번째까지 자르면 [5, 2, 6, 3]입니다.
- 1에서 나온 배열을 정렬하면 [2, 3, 5, 6]입니다.
- 2에서 나온 배열의 3번째 숫자는 5입니다.
- 배열 array, [i, j, k]를 원소로 가진 2차원 배열 commands가 매개변수로 주어질 때, commands의 모든 원소에 대해 앞서 설명한 연산을 적용했을 때 나온 결과를 배열에 담아 return 하도록 solution 함수를 작성해주세요.
제한사항
- array의 길이는 1 이상 100 이하입니다.
- array의 각 원소는 1 이상 100 이하입니다.
- commands의 길이는 1 이상 50 이하입니다.
- commands의 각 원소는 길이가 3입니다.
입출력 예
입출력 예 설명
- [1, 5, 2, 6, 3, 7, 4]를 2번째부터 5번째까지 자른 후 정렬합니다. [2, 3, 5, 6]의 세 번째 숫자는 5입니다.
- [1, 5, 2, 6, 3, 7, 4]를 4번째부터 4번째까지 자른 후 정렬합니다. [6]의 첫 번째 숫자는 6입니다.
- [1, 5, 2, 6, 3, 7, 4]를 1번째부터 7번째까지 자릅니다. [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]의 세 번째 숫자는 3입니다.
소스 코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
import java.util.Arrays;
class PGLevel1Q4 {
public int[] solution(int[] array, int[][] commands) {
int[] answer = new int[commands.length];
for (int i = 0; i < commands.length; i++) {
int[] temp = Arrays.copyOfRange(array, commands[i][0] - 1, commands[i][1]);
Arrays.sort(temp);
answer[i] = temp[commands[i][2] - 1];
}
return answer;
/*
int i = 0;
while (i < commands.length) {
int start = commands[i][0] - 1; // index이므로 -1 처리
int end = commands[i][1] - 1; // index이므로 -1 처리
int selectedNum = commands[i][2] - 1; // index이므로 -1 처리
System.out.println("start = " + start
+ ", end = " + end
+ ", end-start = " + (end - start)
+ ", selectedNum=" + selectedNum);
int arraySize = end - start + 1;
int[] temp;
if (arraySize > 0) {
temp = new int[arraySize];
} else {
temp = new int[1];
}
int count = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < array.length; j++) {
if (count >= arraySize) {
break;
}
if (j >= start && j <= end) {
temp[count] = array[j];
count ++;
}
}
Arrays.sort(temp);
System.out.println("temp=" + Arrays.toString(temp));
answer[i] = temp[selectedNum];
i++;
}
return answer;*/
}
}