두 배열에서 같은 값 찾기
첫번째 풀이
소스 코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
public class IntersectionOfTwoArraysII {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// int[] nums1 = {1,2,2,1};
// int[] nums2 = {2,2};
int[] nums1 = {4,9,5};
int[] nums2 = {9,4,9,8,4};
int[] result = intersect(nums1, nums2);
System.out.print("result: ");
for (int num : result) {
System.out.print(num + ",");
}
}
public static int[] intersect(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
List<Integer> data = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums1.length; i++) {
int num = nums1[i];
for (int j = 0; j < nums2.length; j++) {
int compareNum = nums2[j];
if (num == compareNum) {
data.add(compareNum);
nums1[i] = -1;
nums2[j] = -1;
break;
}
}
}
return data.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();
}
}
풀이
러프하게 이중 포문을 이용한 방법이다.
포문을 돌면서 같은 값이 있는 경우 중복 체크가 되지 않게 하기 위해 -1로 바꿔준다.
또한 같은 값을 찾은 경우 break 문을 통해 그 뒤로는 돌지 않도록 한다.
다만, 이 방법은 만약에 주어지는 배열에 -1이 있는 경우 정상적으로 돌지 않을 것이기 때문에 수정이 필요하다. (릿코드에서는 Accepted 가 되기는 하지만 정답을 맞추는게 목적이 아니니까 !)
최종 풀이
소스 코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
public class IntersectionOfTwoArraysII {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// int[] nums1 = {1,2,2,1};
// int[] nums2 = {2,2};
int[] nums1 = {4,9,5};
int[] nums2 = {9,4,9,8,4};
int[] result = intersect(nums1, nums2);
System.out.print("result: ");
for (int num : result) {
System.out.print(num + ",");
}
}
public static int[] intersect(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
Arrays.sort(nums1);
Arrays.sort(nums2);
List<Integer> data = new ArrayList<>();
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
while (i < nums1.length && j < nums2.length) {
int item1 = nums1[i];
int item2 = nums2[j];
if (item1 == item2) {
data.add(item1);
i++;
j++;
} else if (item1 > item2) {
j++;
} else {
i++;
}
}
return data.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();
}
}
풀이
정렬한 후 두 배열을 한칸씩 이동하며 비교하는 방법이다.
두 값을 비교해서 더 작은 배열의 index를 1씩 증가시킨다.
같은 값을 발견한 경우 두 index 모두 1씩 증가시킨다.
이렇게하면 비교했던 값들은 다시 비교를 하지 않기 때문에 매우(?) 좋은 방법인 것 같다.
아마, return 할 때에 stream() 을 이용하지 않고 직접 for 문을 이용해서 배열로 변환시킨 후 return 하면 속도는 더 빨리 나올 것 같지만 귀찮..으니 그대로 두었다.
결과
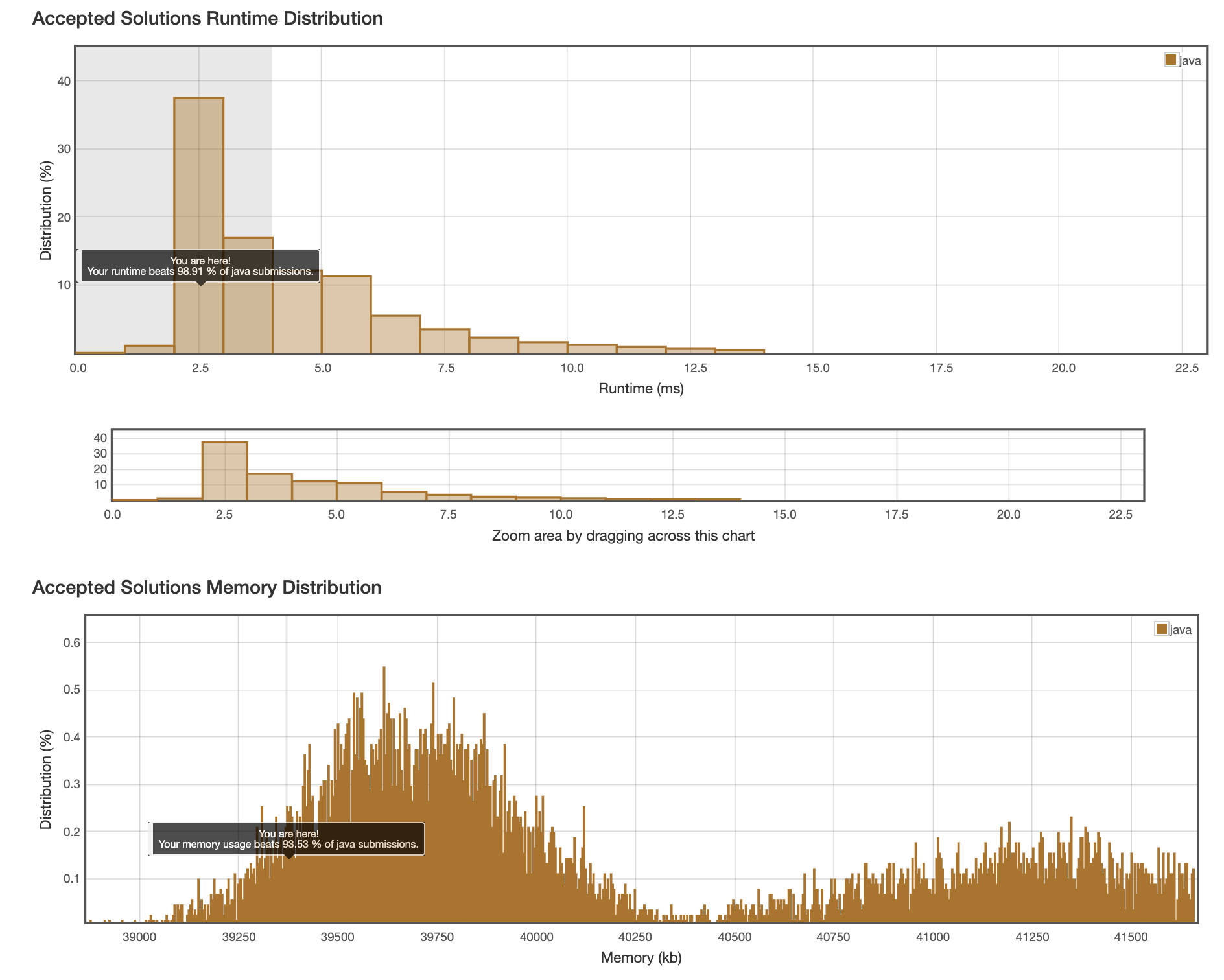
회고
정렬을 했기 때문에 할 수 있는 쉬운 방법이 있었다. 지난 번에는 어떤 자료구조를 사용하느냐에 따라서 난이도가 달라진다고 말을 했었는데 정렬은 배열을 다룰 때에 대한 팁인 것 같다.
정렬을 하냐 안하냐 혹은 사용 해도 되느냐 안되느냐에 따라 더욱 쉽게 문제를 풀 수 있게 되는 것 같다.